Building a multilingual Moodle LMS site sounds simple — until you realize Moodle LMS does not automatically display different versions of a course based on the user’s selected language. Without the right setup, you can easily end up with a mix of duplicate content and content displayed in the wrong language, confusing users and screen readers.
Fortunately, with a few key tools and techniques, you can create a seamless multilingual experience across your Moodle site and courses.
Over the years, I’ve built many multilingual Moodle LMS sites. In this guide, I’ll walk you through the essential steps to make it work smoothly.
1. Install Language Packs
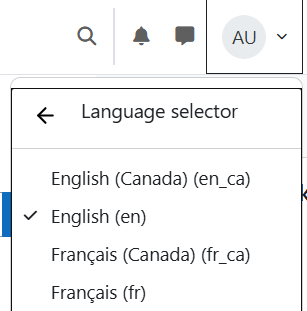
As a site administrator, start by installing a language pack for each language you want to support by navigating to Site Administration > General (tab) > Location (section) > Language Packs (link). Select the languages that you want to add and use the Install Selected Language Pack(s) button to install them.
If you're supporting localized versions of a language (e.g., French Canadian), you’ll need to install both the base language pack (French) and the localized one (French Canadian). To keep the language menu clean, specify exactly which languages you want visible to users by navigating to Site Administration > General (tab) > Location (section) > Language Settings (link). Then add the languages you want to display to the Languages on Language Menu field.
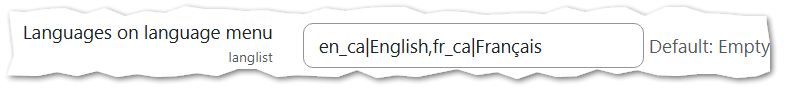
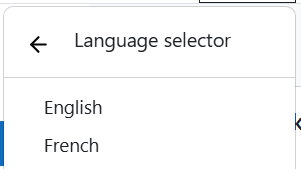
Tip: After saving, if the site's default language is no longer one of the languages in your list, you will need to select a new Default Language on the same page and save again.
Once language packs are installed, Moodle’s menus and interface text will automatically adjust based on each user's selected language. However, Moodle LMS does not automatically translate your course content—you’ll need to manage that part yourself.
2. Add Multi-Language Support with the Content (v2) Filter for Moodle LMS
Moodle LMS has a built-in filter system that processes tagged text content through various filters. This is how you can create multi-language content - content that changes language based on the language of the user interface. The problem is, it uses HTML <span> tags, so you need to edit the HTML to apply the tags.
Unlike the Multi-language Content filter plugin included with Moodle LMS core, Iñaki Arenaza created and maintains the Multi-language Content (v2) filter that uses text-based tags to wrap different language versions of your text.
Multi-Language Content (v2) provides a much simpler and flexible approach:
- Plain text tagging: Tag your content directly while editing. No HTML knowledge needed.
- Visible tags: See the language tags right in the editor, instead of switching to HTML view.
- Shorter tags: Save space, allowing longer course names or supporting more languages in fields with character limits.
- Flexible tagging: Apply tags to inline text or multiple paragraphs of text. You can even wrap images embedded in your content with language tags.
To set it up, install and enable the Multi-Language Content (v2) filter plugin. Then navigate to Site Administration > Plugins (tab) > Filters (section) > Manage Filter (link). Activate the filter for both Content and Headings, and move it to the top of the list of filters to ensure it runs first.
3. Create Multilingual Courses with {mlang} Tags
Moodle LMS doesn't allow entire courses to be hidden or shown based on language, but you can still create multi-language courses by wrapping your course names, section titles and content in {mlang} tags. As a result, only the content that matches the user's current language will be shown. This allows users to view the course in their preferred language, and in most cases, they can switch languages at any time while making their way through the course.
Inline example:
{mlang en}Content in English{mlang}{mlang fr}Contenu en français{mlang}Paragraph example:{mlang en} One or more paragraphs in English. {mlang}{mlang fr} Un ou plusieur paragraphe en français. {mlang}
If you’re using multiple localized language packs for the same parent language, you will need to adjust the tag accordingly. For example:
- French:
{mlang fr}Contenu en français{mlang} - French Canadian:
{mlang fr_ca}Contenu en françaiscanadien{mlang}
If you are just using one localized language per parent language, you should be able to just use the parent language {mlang fr} tag, even though you are actually using fr_ca. If this doesn't work for you, you will need to adjust the Multi-Language Content (v2) plugin setting for Parent Language Behaviour. For more information, see the plugin's documentation.
Tip: Be sure to apply language tags consistently across your site name (in the front page settings), category names, and course names as well. Some themes, like Trema, make it possible to use language tags in Site Administration > Appearance (tab) > Additional HTML (link) > Within Head (field) to conditionally add CSS to your site. For example, you may need to have a different company logo in the header and create language-specific JavaScript depending on the UI language of your Moodle LMS site.
4. Use Activity Restrictions for Files, URLs, and SCORM
Some content types, like URLs, files, H5P and SCORM activities, can’t be easily made multilingual with {mlang} tags alone. For these cases, you can use Restriction by Language plugin by Renaat Debleu you can show or hide specific activities based on the user’s language selection.
With this method:
- Create multiple versions of the module, one for each language.
- Apply a language-based restriction to each activity.
Learners only see the activities available in their selected language.
One limitation:
If you restrict activities by language, learners can't switch languages midway through an activity as they can with {mlang} tagged content.
Course Completion Tip: Restricting activities by language can complicate course completion tracking, since learners complete different sets of activities based on their language. A simple solution is to base course completion on a final common activity, and configure its availability based on the completion of either the English or French (or other language) set of activities.
5. Special Considerations for Multi-Language SCORM Packages
Creating a multilingual SCORM experience requires extra planning. Ideally, you’ll build the language selection menu and all language versions directly inside the SCORM package itself. When possible, I recommend designing SCORM packages as self-contained multilingual experiences.
By following these strategies, you can deliver a seamless, professional multilingual experience for your Moodle learners, without the need to duplicate courses or rebuild content.
Hope you find this information useful.
Michael Milette





Add a comment: